The Linux last command is a useful utility that provides detailed information about the most recent logins to the system. By querying the system’s log files, specifically /var/log/wtmp, it displays a comprehensive list of user sessions, including the username, terminal name, IP address (if applicable), and the time and duration of each session. This command is particularly valuable for system administrators to monitor user activity, track login attempts, and identify unauthorized access. Additionally, last can be customized with various options to filter results, such as showing only a specific user’s logins or displaying entries from a particular date range, making it a versatile tool for system management and security auditing.
If you are new to system administration, you may need to access or monitor credentials. You will probably use several tools for this purpose, and one of them is last. In this tutorial, we will explain the basic functions of this program with some easy-to-understand examples.
Before we get to the explanations, we should mention that all the examples here have been tested on an Ubuntu 24.04 system, but they should work the same way on any recent Linux distribution.
Linux last command
The last command displays a list of the last logged-in users. Following is its syntax:
last [options] [username...] [tty...]
Here is how the man page explains this tool:
last searches back through the /var/log/wtmp file (or the file desig?
nated by the -f option) and displays a list of all users logged in (and
out) since that file was created. One or more usernames and/or ttys
can be given, in which case last will show only the entries matching
those arguments. Names of ttys can be abbreviated, thus last 0 is the
same as last tty0.When catching a SIGINT signal (generated by the interrupt key, usually
control-C) or a SIGQUIT signal, last will show how far it has searched
through the file; in the case of the SIGINT signal last will then ter?
minate.The pseudo user reboot logs in each time the system is rebooted. Thus
last reboot will show a log of all the reboots since the log file was
created.
Following are some Q&A-styled examples that should give you a better idea on how last works.
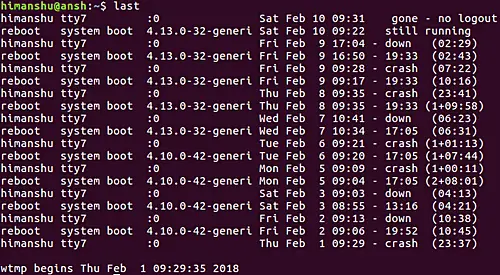
Q1. How to use the last command?
The basic usage is very easy. All you have to do is to run the ‘last’ command sans any options:
last
Q2. How to customize the output in case of non-local logins?
By default, in case of non-local plugins, last command displays output in the following way:
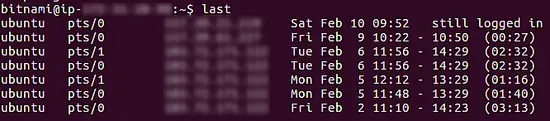
Note: In the screenshot, we have intentionally blurred some parts containing IP addresses.
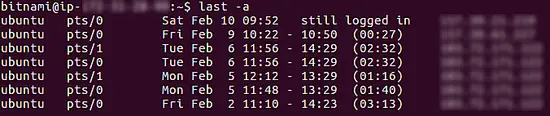
Now, if you want, you can slightly customize this output by moving the IP address related column to extreme right. This can be done using the -a command line option.
Q3. How to make last read a different file?
As already mentioned in the beginning of the tutorial, the last command reads the /var/log/wtmp file to prepare its output. However, if you want, you can make the tool read a completely different file. This you can do using the -f command line option. Of course, you’ll have to pass the new file name (along with its path) as input to this option.
last -f [new-file-path-and-name]
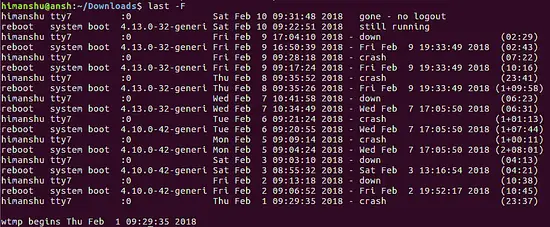
Q4. How to make last print complete date and time info?
If you want last to produce complete date and time information in output, use the -F command line option.
last -F
Q5. How to make last show only a specific number of lines?
If you want to customize the number of lines the last command shows in output, you can do that using the -n command line option. Of course, you’ll have to pass a number to this option as input.
For example:
last -n 3
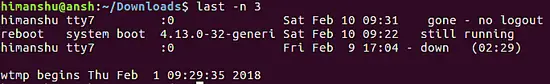
So you can see the output only contains 3 lines.
Q6. How to make last suppress hostname field in output?
The third column in last’s output is hostname information. However, for some reason, if you want the tool to suppress this information, use the -R command line option.
last -R
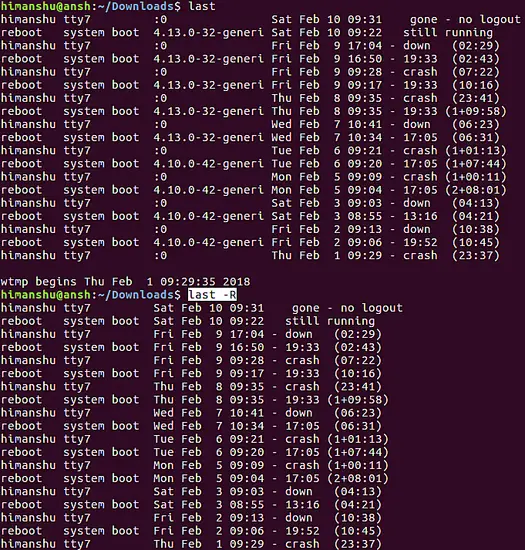
Q7. How to make last display info for a specific time period?
Suppose you want last to only display output based on time – say, only information from yesterday and today – then you ca use the -s and -t command line options.
For example:
last -s yesterday -t today
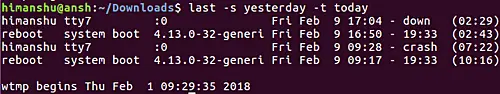
Please note the options that take the time argument understand the following formats:YYYYMMDDhhmmss
YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss
YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm (seconds will be set to 00)
YYYY-MM-DD (time will be set to 00:00:00)
hh:mm:ss (date will be set to today)
hh:mm (date will be set to today, seconds to 00)
now
yesterday (time is set to 00:00:00)
today (time is set to 00:00:00)
tomorrow (time is set to 00:00:00)
+5min
-5days
Q8. How to make last display things like run level changes?
To display information like run level changes and system shut down entries, use the -x command line option.
last -x
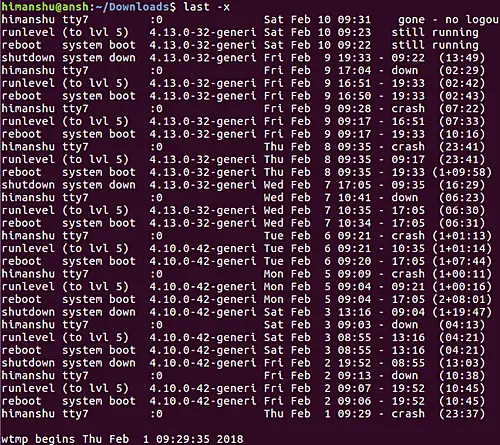
Conclusion
Agreed, last isn’t one of those commands that you’ll use daily, but there will likely be days where this tool would be of great help. We have covered several major options here in this tutorial – should be enough to get you started. For more info, head to the utility’s man page.













