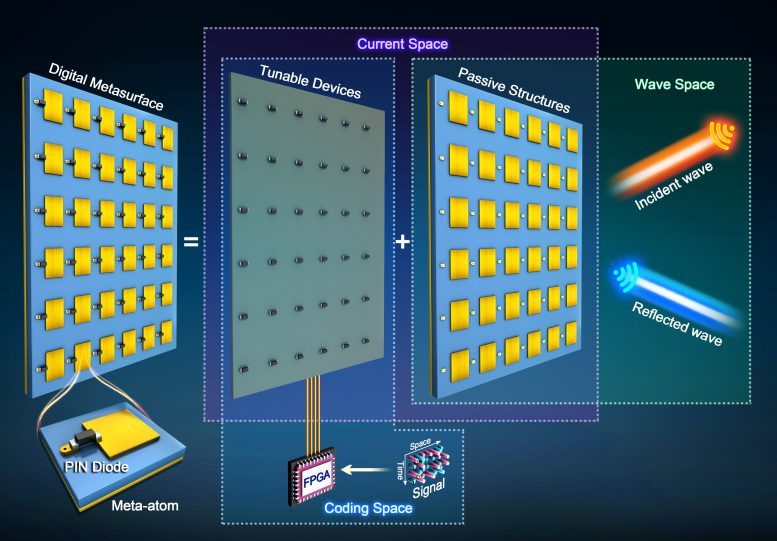
The metasurface is divided into three spaces: the coding space, the current space, and the wave space. The three spaces are composed of the digital control signals and the tunable devices, the currents on the passive structures and tunable devices, and the fields in the region of interest, respectively. Credit: Science China Press
A recent study led by Dr. Ruiwen Shao and Prof. Junwei Wu from the Institute of Electromagnetic Space at Southeast University in Nanjing, China, explores the intricate dynamics of scattered waves in digital metasurfaces. Utilizing the technique of singular value decomposition (SVD), Dr. Shao discovered a fascinating discrepancy: the count of non-zero singular values does not precisely match the number of meta-atoms within the metasurface. Instead, it is approximately equal, shedding light on the complex behavior of these electromagnetic structures.“This is a very unusual result, which is contrary to the previous modeling method of metasurface,” Shao says.
Ruiwen Shao and Junwei Wu, together with lab director Tiejun Cui, sought to determine what causes the redundant singular value. The team regards the digital coding metasurface as a microwave network consisting of two networks, including passive structures and tunable devices. The composition successfully separates the impact of the coding states on the scattered waves. “The expression obtained by microwave network cascade formula still contains matrix inversion term, so we naturally wonder whether power series expansion will have an effect on the simplification.” Wu says.
The team found that after a series of derivations and approximations, the scattered waves of the digital coding metasurface can be expressed as a second-order polynomial of the coding states, including constant term, first-order terms, and second-order terms of adjacent codes. “The introduction of the zero-order term and the second-order terms doubles the rank of the equation, which is consistent with the number of non-zero singular values. These terms can be considered to be caused by the mutual coupling of adjacent meta-atoms.” Shao says.
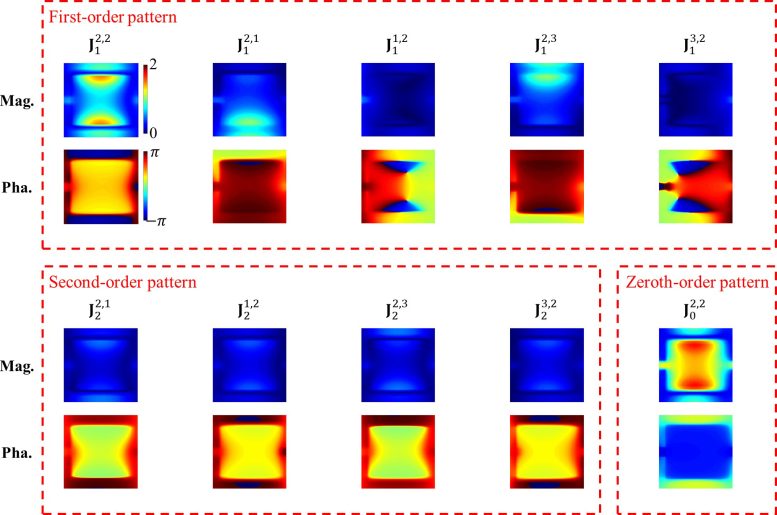
The constant term and first-order pattern of the central element dominate the current of the meta-atom. The first-order patterns of the upper and lower adjacent elements take second place, and the remaining ones are relatively small. Credit: Science China Press
Practical Applications and Conclusion
The researchers extracted these current patterns through full-wave simulations. Based on the patterns, they accurately predict the scattered EM waves of the metasurface in any coding state. “A high-precision semi-analytical expression provides a powerful tool for us to study the statistical characteristics of metasurfaces theoretically. With the help of the macroscopic model, the mutual coupling of elements is transformed into current covariance. Therefore, we finally found that the probability distribution of current on the metasurface is a set of dependent normal distributions. We compare the differential entropy of dependent distributed currents with that of independent and identically ones, and the difference between them indicates the information loss of converting digital signals into electromagnetic waves.” Wu says.
How to evaluate the capability of the metasurface to transmit information is an urgent problem to be solved in the application of metasurface communication systems. In this study, the researchers provided a novel method of quantitative the information loss caused by mutual coupling. Consistent with the common cognition, the information loss increases as the element period decreases.
Reference: “Macroscopic model and statistical model to characterize electromagnetic information of a digital coding metasurface” by Rui Wen Shao, Jun Wei Wu, Zheng Xing Wang, Hui Xu, Han Qing Yang, Qiang Cheng and Tie Jun Cui, 29 November 2023, National Science Review.
DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwad299













